Foreign Direct Investment in Nepal
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ Home
This page is under construction!
General FDI Information:
Q1. How is Foreign Investment defined in Nepal?
“Foreign investment” means the following investment made by a foreign investor in an industry or company:
(1) Foreign currency,
(2) Re-investment in an industry of dividends derived from foreign currency or shares,
(3) Lease finance made of certain assets of aircraft, ship, machinery and equipment, construction equipment or similar other equipment,
(4) Investment in venture capital fund,
(5) Investment in listed securities through secondary securities market,
(6) Investment by purchasing shares or assets of a company incorporated in Nepal,
(7) Investment received through the banking channel after issuing securities in a foreign capital market by an industry or company incorporated in Nepal,
(8) Investment made through technology transfer, or
(9) Investment maintained by establishing and expanding an industry in Nepal
(Source:
FITTA, 2019 Sec 2 (j) )
Q2: Who qualifies as a foreign Investor?
"Foreign investor" means any foreign individual, firm, company, Non-resident Nepali or foreign government or international agency or other corporate body of similar nature that makes foreign investment, and also includes, in the case of a foreign investor that is an institutional foreign investor, the ultimate beneficiary of such an institution.
Source: FITTA, 2019 Section 2(k)
Q3: Why invest in Nepal?
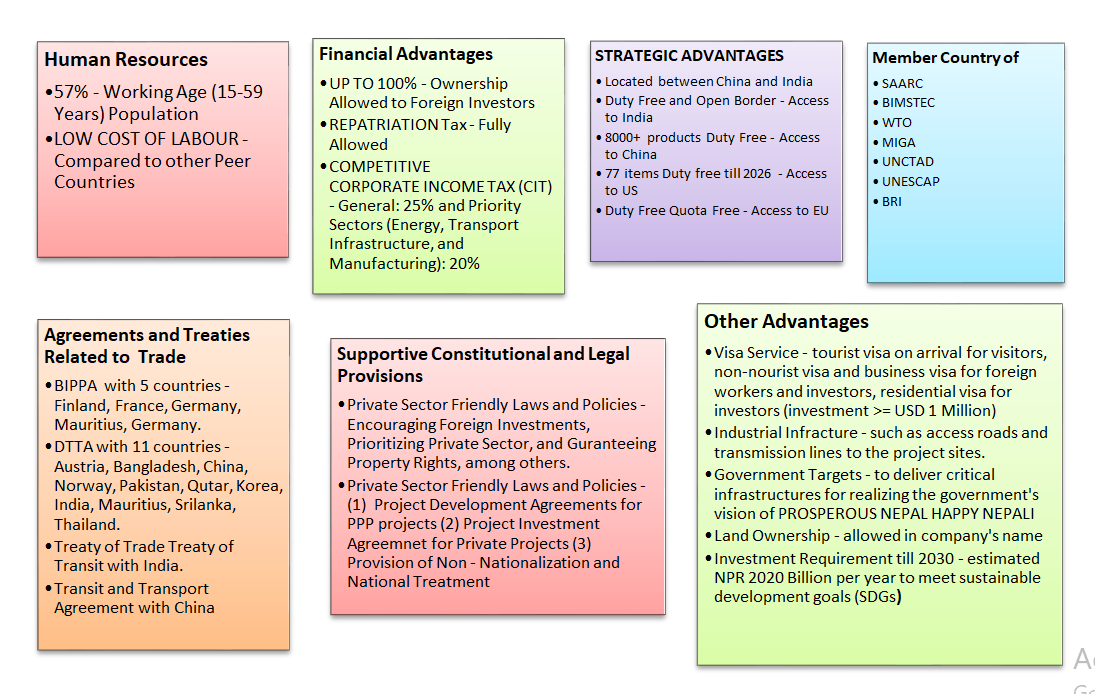
Chart reference - Investment Board Nepal (IBN)
Q4: What are the prospective areas of FDI in Nepal?
Based on the national priority, the major sectors for the FDI are:
a) Hydropower of Renewable Energy (Production and Transmission)
b) Infrastructure related to Transportation (Fast Track, Railway, Tunnel, Cable Car, Metro Rail, Flyover and International Airport)
c) Agricultural, Food Procession and Herbs Procession Industries
d) Tourism Industries
e) Digital Economy & ICT
f) Mineral and Productive Sector Industries
g) Manufacturing and Industrial Zones
g) Health and Education
Legal and Regulatory Framework
Q5: What are the key acts/laws/Policies concerning FDI in Nepal?
FDI in Nepal is primarily governed by the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act (FITTA), 2019 and Industrial Enterprises Act, 2020. Complemented by the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Rules, 2021 and Industrial Enterprise Rules, 2078. Several other relevant acts pertaining to FDI are also listed below:
A. Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act (FITTA), 2019
FITTA 2019 provides a clear framework for foreign direct investment (FDI) in Nepal, covering types of foreign investment, approval processes, investment protections, dispute resolution, and incentives aimed at attracting and regulating foreign investments.
Eng : https://ibn.gov.np/resources/details/the-foreign-investment-and-technology-transfer-act-2019-english-6187
B. The Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Rules, 2021
It provides detailed guidelines for the implementation of the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 2019 (FITTA). It clarifies procedures, processes, and regulatory requirements for foreign investment and technology transfer in Nepal.
Nepali: https://doind.gov.np/uploads/notices/Notices-202106011317126.pdf
C. The Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Rules, 2021
It provides detailed guidelines for the implementation of the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 2019 (FITTA). It clarifies procedures, processes, and regulatory requirements for foreign investment and technology transfer in Nepal.
Nepali: https://doind.gov.np/uploads/notices/Notices-202106011317126.pdf
D. Industrial Enterprises Act, 2020
The Industrial Enterprises Act, 2020 focuses on promoting industrial growth, simplifying business procedures, and encouraging both foreign and domestic investment. It offers incentives to industries and outlines clear processes for foreign investors to operate and repatriate profits in Nepal. https://moics.gov.np/content/9291/9291-industrial-enterprises-act-20/
English :https://doind.gov.np/detail/196
E. Industrial Enterprises Rules, 2078
Focuses on implementing provisions of the Industrial Enterprises Act, 2020 by simplifying procedures for business registration, licensing, and incentives for industries. https://doind.gov.np/uploads/notices/Notices-20220405201944826.pdf
F. Public Private Partnership and Investment Act, 2019
The Act provides a legal framework for partnerships between the government and private entities, encouraging investment in sectors like infrastructure, energy, transportation, and social services.
Nepali: https://doind.gov.np/detail/106
English: https://ibn.gov.np/resources/details/public-private-partnership-and-investment-act-2019-english-6187
G. The Company Act, 2006
The Company Act of 2006 A.D. is primarily concerned with the establishment and operation of companies existing in Nepal. It also specifies requirements for registering a company in Nepal. https://moics.gov.np/content/9292/9292-company-act-2063/
Unofficial English Act : https://actnepal.com/en/act/1/1/companies-act-2063-2006
H. Nepal Rastra Bank Foreign Investment and Foreign Loan Management Bylaw, 2021
https://www.nrb.org.np/contents/uploads/2019/12/NRB-FIFL-Bylaw_English.pdf
I. Labor Act, 2074
It provides the legal framework for regulating labor relations, protecting workers' rights, and ensuring fair employment practices including work permit approval for foreign citizen.
https://moless.gov.np/content/11121/11121-%E0%A4%B6%E0%A4%B0%E0%A4%AE-%E0%A4%90%E0%A4%A8-%E0%A5%A8%E0%A5%A6%E0%A5%AD%E0%A5%AA/
Unofficial Eng : https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/NEP225978.pdf
J. Special Economic Zone Act. 2073
This act is made to regulate the establishment, operation and management of special economic zone.
English: https://www.doind.gov.np/detail/198
Note: Laws can be accessed through the official website of Nepal Law Commission or the website of Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Supplies. (Official archives of Nepal's Constitution, Statues / Acts, Ordinance, Formation Orders, Rules and Regulations, Policies, International Treaties, Historical Documents
Q6: What are the Government and Private Sector Agencies of Nepal related to FDI process?
| S.N |
Agencies |
Major Functions |
| 1. |
FNCCI (Federation of Nepalese Chamber of Commerce and Industries) |
FDI Help desk will ensure that investors are well informed about the policy and processes related to FDI in Nepal. |
| 2. |
Ministry of Industries, Commerce and Supplies |
Formulate policies and laws regarding FDI |
| 3. |
Industry and Investment promotion Board |
Provide consent to industries that require permission |
| 4. |
Investment Board of Nepal |
Approve the foreign investment exceeding NRs. 6 billion and provide other facilitation |
| 5. |
Department of Industry( One Stop Service Center) |
Approve the foreign investment not exceeding NRs. 6 billion and provide industry administration related services |
| 6. |
Office of Company Registrar |
Register company and provide administration related services |
| 7. |
Nepal Rastra Bank (Central Bank of Nepal) |
Provide approval for bringing in foreign currency against approved investment, recording, and repatriation |
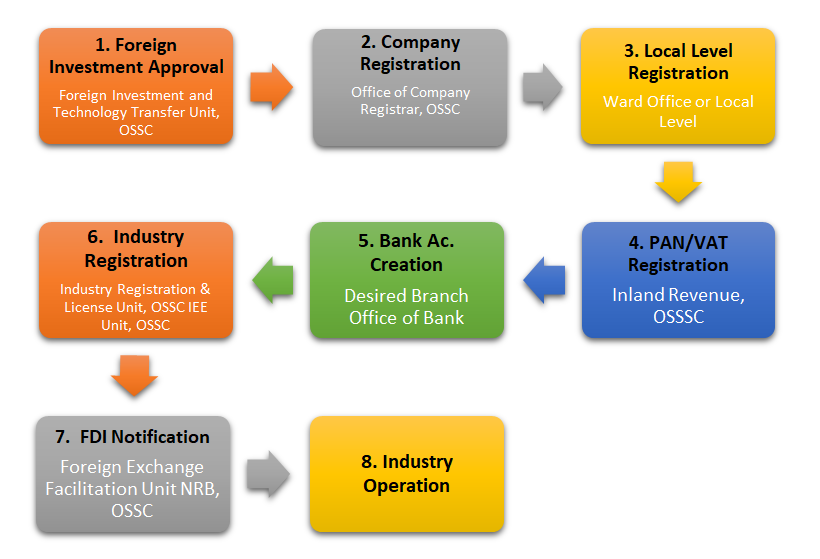
Q7: FDI Registration Process Flowchart
Nepal, typically, the initiation of any industry begins with FDI approval. This is succeeded by the processes of company registration, local level registration, setting up a bank account, and obtaining VAT/PAN registration. Subsequently, investors are required to receive a notification letter from Nepal Rastra Bank for investment inflow. Finally, the industry must undergo registration at the Department of Industry, including any necessary licensing based on the proposed products and services. The diagram below visually represents the approval and licensing steps.
*OSSC – One Stop Service Center
Q: Where do we obtain authorization for foreign investment?
According recent amendment in investment related laws, FDI approvals, previously required from the Investment Board for investments exceeding NPR 6 billion, can now be obtained directly from the Department of Industry (DOI), whereas National Pride Projects and Public Private Partnership Projects need to be approved by the Investment Board of Nepal (IBN).
Q: Is there any faster way to get FDI Approval in Nepal?
Yes
, Foreign investors can apply through the automatic route to:
- Establish a new company with 100% ownership or a joint venture with a total capital of up to NPR 500 million.
- Increase capital in an already established foreign-invested company.
Approval is granted automatically for these investments through the given link.
https://imis.doind.gov.np
Q: What is the procedure for the establishment and operation of FDI in Nepal?
- Obtaining Foreign Investment Approval from DOI or NIB
- Incorporation of Company at the Office of the Company Registrar
- Tax Registration at the Inland Revenue Office
- Business Registration at the Local Ward Office
- Registration of Industry at the DOI
- Obtaining Non-Blacklist Certificate from Credit Information Bureau
- Obtaining approval from NRB to infuse the Investment Amount
- Infusion of investment amount in local bank and obtaining Investment Certificate
- Recording of the infused investment amount at the NRB
Q: What are the Documents Required for Approval of Foreign Investment? Rule 8, FITTR, 2022
1. For Foreign Investment:
- Project Introduction & Investment Plan - Two parts.
- Joint Investment Agreement - If multiple investors, submit two copies.
- Natural Person Investor Documents - Passport and personal details (biodata).
- Foreign Company Investor Documents - Certificate of incorporation, articles of incorporation, directors’ and shareholders’ documents, company profile, and managing director’s financial statement.
- Joint Investment Documents - Data certificate, partner details, partner agreement, and company profile.
- Nepali-Origin Foreign Citizen or NRN Documents - Required verification documents.
- International Organization Documents - Organizational statement, director’s introduction, profile, and relevant institutional data.
- Absentee Investor Documents - Letter of intent and a document detailing investment intent.
- Foreign Investment Certificate - Issued by the investor’s foreign bank.
- Additional Documents - As requested by the approving authority.
2. For Foreign Investment in an Existing Industry by Share Transfer:
- Application from the share transferor Share transfer agreements – 3 copies (Original)
- Copy of minutes of the meeting of Board of Directors of Nepali Company – 1 copy
- Notarized copy of the minutes of Board meeting, Certificate of Incorporation, Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association and Company Profile, if the foreign party is a Company – 1 copy
- Notarized copy of Passport and Biodata of foreign party, if the party is an individual– 1 copy
- Financial Credibility Certificate of the Foreign Investor issued by a bank– 1 copy, Current Share Holders’ List as recorded in the Office of Company Registrar- 1 copy and
- Audit Report – 1 copy
- Tax Clearance Certificate – 1 copy
- Letter of Authorization to be signed on behalf of the Company – 1 copy
- Certificate of industry/company registration – 1 copy
3. For Lease Investment in an Existing Industry:
- Industry registration certificate and the copy of the approved project proposal
- Lease agreement stating clearly the time, value and payment procedure of the lease- 2 copies
- If the lessor is a foreign individual, notarized copy of the passport and biodata
- If the lessor is a company, company registration certification, Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association, minute of the decision of the board and Company Profile
- Documents exhibiting the value of the Airplanes, Ship, Machines, Building Equipment or other devises to be given in lease.
- Insurance documents of the Airplanes, Ship, Machines, Building Equipment or other devises to be brought in lease
- Other documents as required by the investment approval agency
4. For Foreign Investment through Technology Transfer
- Technology Transfer Agreement – 3 copies
- Notarized copies of Certificate of Incorporation, Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association of the domestic company – 1 copy
- Notarized copy of the passport of foreign investor or Certificate of Incorporation, Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association if the foreign party is a company – 1 copy
- Foreign investor’s Bio-Data or company profile
- Minutes of the meeting of Board of Directors from concerned companies for Technology Transfer
- Letter of Authorization from the company
- Notarized copy of current Audit Report and Tax Clearance Certificate of the domestic company
Q: What is the Fee structure for approval process of the foreign investment?
There is no fee for FDI approval by the Department of Industry. However, NPR. 20,000 has to be deposited by a new foreign investor as a refundable fund.
Q: By when must the investor bring their investment into Nepal after receiving approval?
(Rule 9 of FITTR)
The investor must bring their investment into Nepal within 1 year of receiving the investment approval.
a) Minimum Investment: At least 25% of the approved amount.
b) Investments up to NPR 250 million: At least 15% of the approved amount.
c) Investments above NPR 25 million to NPR 100 million: At least 10% of the approved amount.
d) Investments above NPR 100 million: At least 5% of the approved amount.
Q: What is the time for completion of the approval process?
It generally takes around 1 to 2 months for the completion of the entire FDI and the incorporation process.
Note: Please check with the Department of Industry of Nepal
Q: What are the Documents required for the company’s registration?
To start a business in Nepal, investors need to incorporate a company. The agency responsible for the incorporation of a company is the Office of the Company Registrar (OCR) under the Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Supplies. The Company Act 2006 provides for incorporation of companies.
- Memorandum of Association (2 sets)
- Approval for Foreign Investment from respective agency (1 copy)
- Articles of Association (2 sets)
- Passport of the Authorized Person of the Company (1copy)
- If the foreign investor is a company, Company registration certificate of the said company and decision of the board of the directors of the said company to make investment in the new company (1 copy)
- JVA agreement and approval from DOI in case of joint venture investment between two companies (1 copy)
- Citizenship of the Witness (1 copy)
- Power of Attorney issued in favor of the Advocates associated with registration (1 copy)
Q: Is foreign investment allowed in all sectors?
There are certain restrictions on few businesses and industries. Here are the Industries or Businesses Restricted for Foreign Investment:
a. Industries, except the large Industries exporting at least seventy-five percent of their own products, in the sectors of animal husbandry, fisheries, beekeeping, fruits, vegetables, oilseeds, pulses, dairy business and other.
Note: *Amended Through the Act related to Investment Facilitation (Nepal Gazette
b. Industries or business related to primary products of agriculture.,b. Cottage and small industries. However, no restriction is placed on transfer of technology in cottage industries.
c. Personal service business (hair cutting, tailoring, driving etc.),
d. Industries manufacturing arms, ammunition, bullets and shell, gunpowder or explosives, and nuclear, biological and chemical (N.B.C.) weapons; industries producing atomic energy and radio-active materials,
e. Real estate business (excluding construction industries), retail business, internal courier service, local catering service, moneychanger, remittance service,
f. Travel agency, guide involved in tourism, trekking and mountaineering guide, rural tourism including homestay,
g. Business of mass communication media (newspaper, radio, television and online news) and motion picture of national language,
h. Management, account, engineering, legal consultancy service and language training, music training, computer training,
i. Consultancy services having foreign investment of more than fifty-one percent.
Q: How are industries classified in Nepal? (Definition of Industries):
a. Micro-industry
- with the fixed capital not exceeding two million rupees, excluding house and land;
- the entrepreneur himself or herself is involved in the operation and management of the industry;
- with a maximum of nine workers including the entrepreneur;
- with annual transaction of less than ten million rupees;
- with the capacity of electric energy,fuel or other oil engine to be consumed by the engine, equipment or machine, if any, used being twenty KW or less.
b. Cottage industry
- based on traditional skills and technology;
- labour-oriented and based on specific skills or local raw materials and local technology, arts and culture;
- withthe capacity of electric energy to be consumed by the engine, equipmentormachine, if any, used being up to fifty KW;
- any industry mentioned in Schedule-2.
c. Small industry:
- An industry with the fixed capital not exceeding one hundred fifty million rupees, other than a micro enterprise and cottage industry;
d. Medium industry:
- An industry with the fixed capital exceeding one hundred fifty million rupees but not exceeding five hundred million rupees;
e. Large industry:
An industry with the fixed capital exceeding five hundred million rupees.
Source: Chapter 3 Section 17 of IEA,2020










